02. Refresher on Signals
heading
Refresher on Signals
ND320 C4 L1 02 What Is A Signal-
Signals Review
Summary
A signal is simply a series of numbers (e.g. [3, 4, 6, 2, 4] is a signal!). Typically these numbers represent a voltage that changes with respect to some physical phenomenon. When the voltage signal changes in time, it’s called a time series signal. Signal processing helps us analyze this sequence of numbers so we can learn more about the physical phenomenon it represents.
image
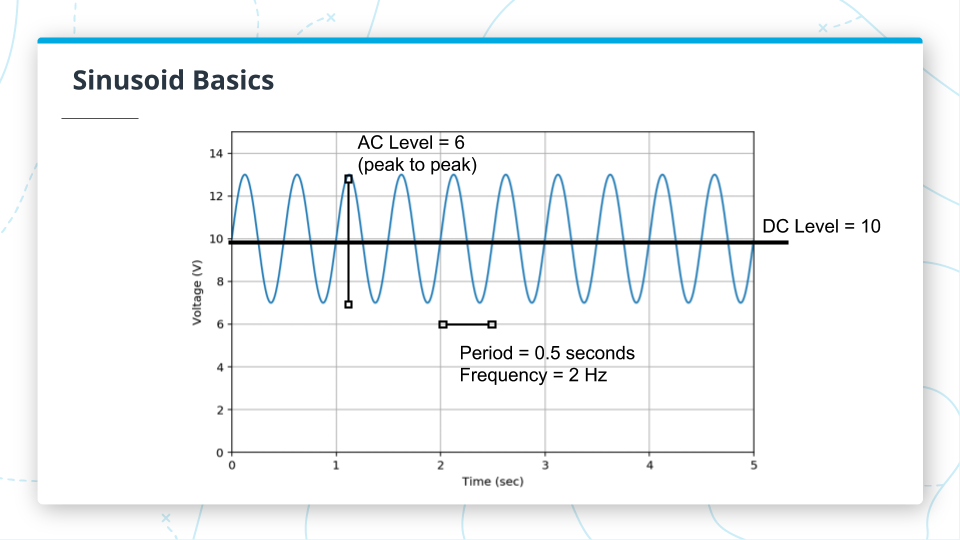
Sinusoid Basics
summary
We can use the figure above to explore some properties of signals. The time-invariant part of the signal is the DC level or mean value (black line), here it’s at 10 Volts. The AC component (blue line) is the part of the signal that varies with time. There are many ways to measure the AC component -- e.g., standard deviation, variance, or interquartile range. In this case, we measured the peak-to-peak amplitude, which is 6 volts.
This signal is also periodic, meaning that it repeats itself over and over again. The period is the amount of time it takes to make one repetition, which in this case is half a second. The frequency is the inverse of the period, or the number of repetitions per second, which is 2 hertz (Hz).
phase change
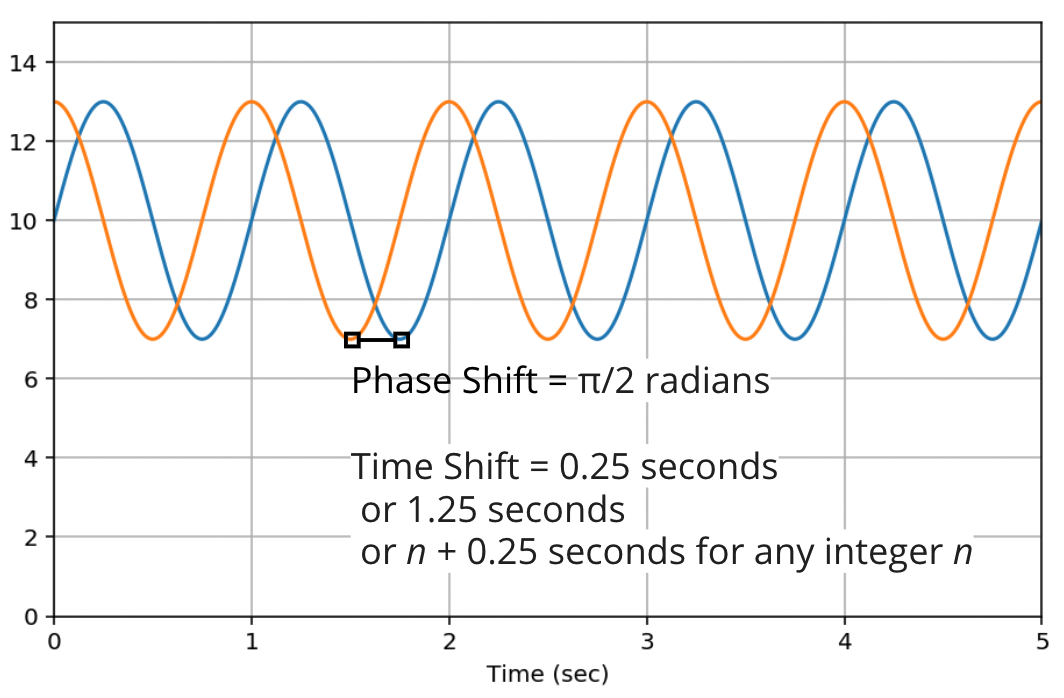
Phase Change
phase change and new vocab
The last property of a periodic signal is the phase shift, which is similar to a time shift. If two signals are time shifted by one full period, there is no difference between them. For this reason, we express this shift by the fraction of the period that they are shifted. If a signal is shifted by a quarter of a period, we can say the phase shift is 90 degrees (360 being a full period). You can also measure phase shift in radians and there are 2 pi radians in a full period. So this phase shift would be half pi radians.
New Vocabulary
- Period: The amount of time it takes to make one repetition.
- Frequency: The amount of repetitions in a given time period, usually 1 second is the time period.
- Hertz (Hz): The units of the sampling rate. 1Hz means 1 sample per second.
- Phase Shift: The shift between two similar periodic signals expressed in fractions of a period (multiplied by 2𝛑 radians or 360°).